The legal ownership of intangible assets, such as inventions, literary and artistic works, designs, symbols,…
Trademark Registration vs. Copyright Registration: What’s the Difference and When to Choose Each.
When it comes to safeguarding your intellectual property, trademark registration, and copyright registration are the two most common forms of legal protection.
Although both serve to protect your creative work, there are important differences between the two. In this blog post, we will explore the differences between trademark registration and copyright registration, and when it is appropriate to choose each.
Trademark Registration:
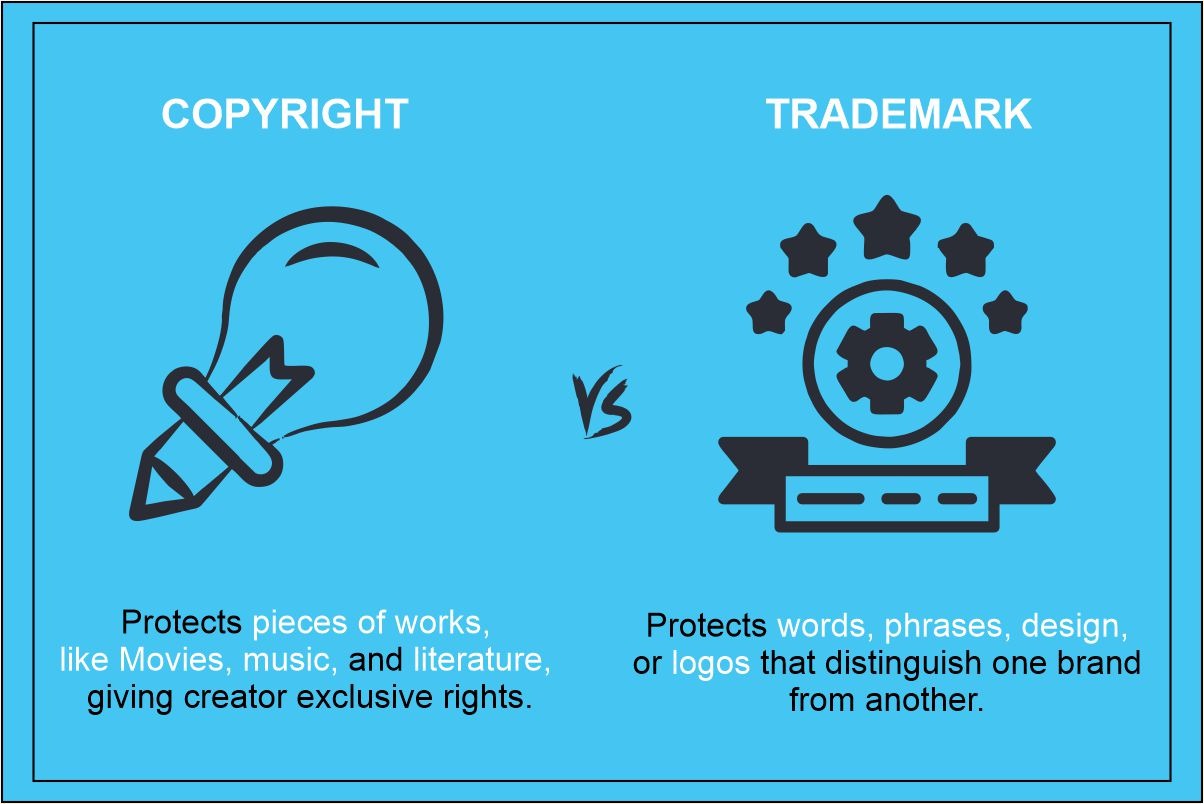
A trademark is a word, symbol, or phrase that identifies and distinguishes the source of a product or service from others.
Trademark registration grants the owner exclusive rights to use the mark in connection with the goods or services identified in the registration.
For instance, Nike’s “swoosh” logo is a trademark that identifies the source of Nike’s athletic shoes and apparel. By registering the mark, Nike has the exclusive right to use the mark on such products and can prevent others from using a similar mark in a similar and confusing manner.
Copyright Registration:
Copyright protects an author’s original work, such as books, music, art, and software.
Registering a copyright provides the owner with the exclusive right to reproduce, distribute, display, and perform the work, as well as to create derivative works based on the original.
For example, a photographer who captures a sunset owns the copyright to that photo.
By registering a copyright, the photographer has the exclusive right to reproduce the photo, display it on their website, or sell prints of the photo.
Difference between Trademark and Copyright Registration:
While trademarks and copyrights protect intellectual property, there are several key differences between the two:
What is protected?
Trademark registration safeguards a sign, word, or phrase that identifies a product or service. Copyright registration safeguards an author’s original work, such as books, music, art, and software.
What rights are granted?
Trademark registration grants the owner exclusive rights to use the mark in connection with the goods or services identified in the registration.
Copyright registration grants the owner the exclusive right to reproduce, distribute, display, and perform the work, as well as to create derivative works based on the original.
How long does the protection last?
Trademark protection can last indefinitely, as long as the owner continues to use the mark in connection with the identified goods or services and takes steps to maintain the registration.
Copyright protection lasts for the life of the author plus 70 years.
When to Register a Trademark?
Registering a trademark is a good option when you have a word, symbol, or phrase that identifies a product or service and you want to prevent others from confusingly using a similar mark.
Trademark registration is particularly important for businesses that rely on brand identity to drive sales.
When to Register a Copyright?
Copyright registration is a good option when you have an original work that you want to protect.
Registering copyright grants the owner the right to reproduce, distribute, and create derivative works based on the original. This may be particularly significant for authors, musicians, and other creatives.
Conclusion:
Trademark registration and copyright registration are two essential tools for safeguarding intellectual property, but they serve different purposes.
Trademark registration aims to protect a word, symbol, or phrase that identifies a product or service, whereas copyright registration safeguards an author’s original work.
Understanding the differences between the two can assist you in selecting the appropriate form of protection for your creations.



This Post Has 0 Comments